Yann Ciarán Ryan
Time and Place: Thursday, 01.07., 11:35–11:55, Room 2
Session: Networking Correspondences
Archives have become essential components in the ‘laboratories’ of those doing historical network research, rendering us with the metadata and digitised collections for computational experiments. However, we have not always taken the time to understand how these sources have come into being (Walsham 2016). Historical correspondence archives, in particular, have been a rich source of relational data on which to base historical network research (for example Błoch, Vasques Filho, and Bojanowski 2020; Ahnert and Ahnert 2019). While authors often reference the fragmentary nature of their archives as a way of encouraging caution regarding their interpretations, the size, shape and gaps in these sources are rarely discussed in the quantitative terms now often used with other sources, such as web archives (Brügger 2018, 74).
Outside of the digital humanities, the ‘archival turn’—an approach which considers an archive as not a neutral collection but rather a text in its own right, one which is what Penman (2016) calls ‘the product of a multiplicity of interventions’—has become an important area of scholarship. This paper argues that if an archive can be considered a text, then it can itself be the subject of the ‘macroanalysis’ long espoused by digital humanities practitioners (Jockers 2013). Rather than using correspondence archives to extract and analyse the networks found within them, this paper will outline how network methods can be leveraged to write or update histories of archives themselves. Using network analysis, it will examine two seemingly-different sets of sources, assembled at different times, and give some specific examples of how network analysis can aid the understanding of the historical contingencies and collection practices which caused these archives to have the structure and shape they do.
The Networking Archives project, from which this work arises, is analysing metadata from three separate sets of Early Modern (1500-1800) correspondence, which have been cleaned and reconciled extensively: the Tudor and Stuart State Papers, and Early Modern Letters Online (EMLO). Together, they form a dataset of c. 450,000 letters, and can be represented as a graph of over 60,000 nodes and 100,000 edges, with substantial overlap between them. It is perhaps the largest historical correspondence dataset so far assembled in one place, but the constituent parts are ultimately from reassembled, partial sources. One, EMLO, is the product of a twenty-first century effort to collect and combine a wide range of epistolary sources relating to the Republic of Letters, whereas the other two are the ‘official’ archives of the working papers of the English Secretaries of State. Despite this official status of the latter, the history of the State Papers is complex: the lines between public and private documents were blurry, and many papers which should have been part of the archive were lost or kept in private hands and not reunited with the rest for several centuries—the Conway Papers being one example (Smith 2014). The result is that despite these very different origins, when analysed as a network, the archives share many similar properties—for example, the degree distribution of each looks remarkably similar and is roughly ‘scale-free’ (figure 1) .
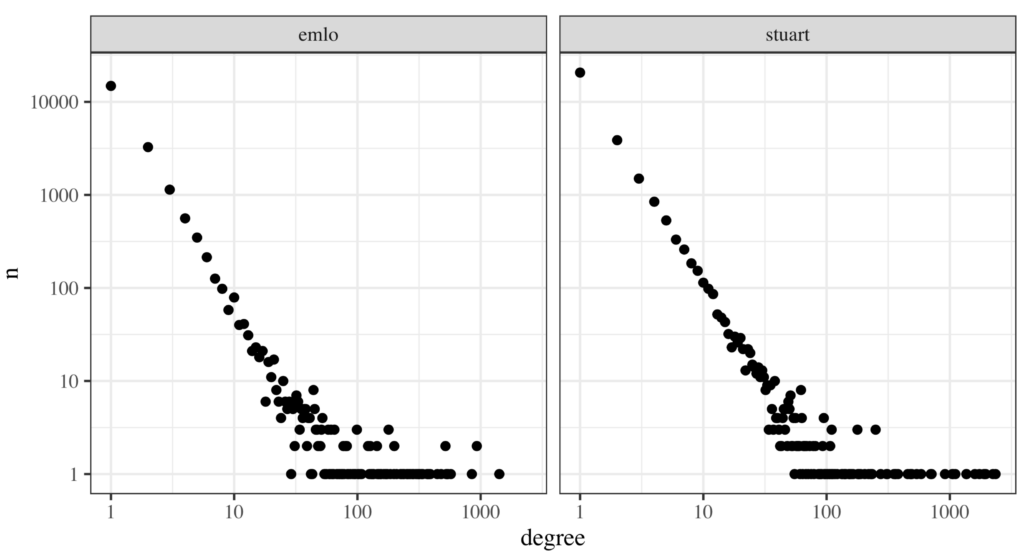
The paper describes how some key network analysis methods and concepts—degree, strength, clustering coefficient, connected components and the rich club—might be used to understand the shape and structure of archives at an aggregate level. It will show how connected and disconnected components, for example, can highlight caches of confiscated family papers and bundles of correspondence seized from captured ships. It will describe how some basic network metrics—degree and weighted degree— when considered on a global scale, can serve as a useful comparative measure to understand the ‘type’ of archive in question, particularly when the direction of the links are considered. An analysis of the clustering coefficient of the SPO and EMLO data will highlight the extent to which, on the whole, these are tightly-linked sources, and the extraction of the rich club and rich club coefficient will be used to suggest the extent to which each is an archive of ‘elites.’ The paper will also—briefly—discuss the use of network analysis to measure the gaps present in an archive, and outline how this might help us to estimate portions of missing data and assess its impact on quantitative network results.
Applying network tools to the study of entire archives has revealed that even seemingly-homogeneous sources such as the State Papers should be considered as partial, reassembled and based on contingency. It follows that rather than think about each as individual silos, they should be viewed as an overlapping set, a fact which allows comparisons between them on an aggregate level. The paper will argue, moreover, that network tools allow us to ignore or supplement the often-artificial boundaries of archives—the catalogues, series or folios in which they have been collected and ordered—and reshuffle the sources in any way we see fit. It will consider the opportunities and pitfalls of this way of thinking about historical archives, and the impact it may have in the field of historical network research.
Works Cited
Ahnert, Ruth, and Sebastian E Ahnert. 2019. “Metadata, Surveillance and the Tudor State.” History Workshop Journal 87: 27–51. https://doi.org/10.1093/hwj/dby033.
Brügger, Niels. 2018. The Archived Web: Doing History in the Digital Age. Cambridge, Massachusetts: The MIT Press.
Błoch, Agata, Demival Vasques Filho, and Michał Bojanowski. 2020. “Networks from Archives: Recon structing Networks of Official Correspondence in the Early Modern Portuguese Empire.” Social Networks, September. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socnet.2020.08.008.
Jockers, Matthew L. 2013. Macroanalysis: Digital Methods and Literary History. University of Illinois Press. https://www.jstor.org/stable/10.5406/j.ctt2jcc3m.
Penman, Leigh T. I. 2016. “Omnium Exposita Rapinæ: The Afterlives of the Papers of Samuel Hartlib.” Book History 19 (1): 1–65. https://doi.org/10.1353/bh.2016.0000.
Smith, Daniel Starza. 2014. The Curious History of the Conway Papers. Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199679133.003.0007.
Walsham, Alexandra. 2016. “The Social History of the Archive: Record-Keeping in Early Modern Europe.” Past & Present 230 (November): 9–48. https://doi.org/10.1093/pastj/gtw033.